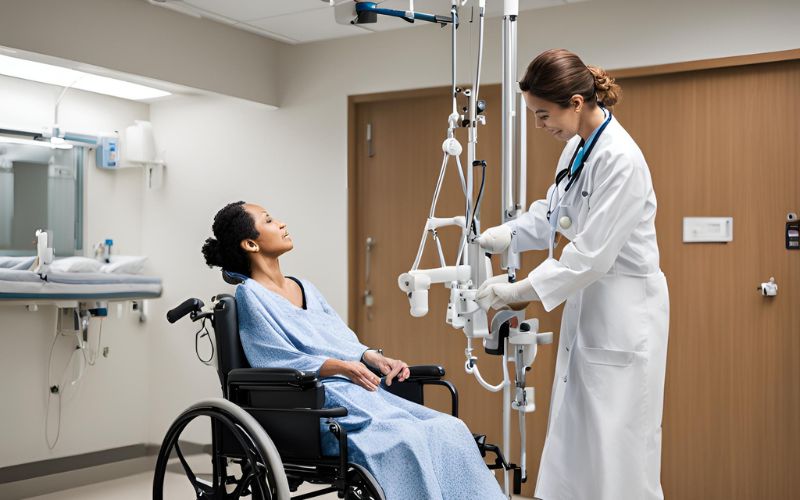
Patient transfers are a critical component of caregiving, whether in hospitals, nursing homes, or home settings. For individuals with limited mobility, these transfers can pose significant risks to both the patient and the caregiver. Powered patient hoists offer a solution that prioritizes safety, dignity, and efficiency. This blog post explores the importance of using powered patient hoists and how to ensure safe transfers.
The Crucial Role of Powered Patient Hoists
Traditional manual lifting techniques can lead to back injuries for caregivers and discomfort or injury for patients. Powered patient hoists eliminate the need for manual lifting, reducing strain and minimizing the risk of accidents. These devices use electric or hydraulic power to lift and transfer patients smoothly and safely.
Key Benefits of Powered Patient Hoists:
- Reduced Risk of Injury: Eliminates manual lifting, protecting both caregivers and patients.
- Enhanced Patient Dignity: Provides a more comfortable and respectful transfer experience.
- Increased Caregiver Efficiency: Simplifies the transfer process, saving time and effort.
- Improved Patient Comfort: Minimizes discomfort and anxiety during transfers.
- Greater Independence: Enables patients to participate more actively in their care.
Ensuring Safe Transfers: Best Practices
While powered patient hoists offer significant advantages, safe operation is paramount. Here’s a comprehensive guide to ensuring secure transfers:
- Proper Training and Competency:
- Caregivers must receive thorough training on the specific hoist model being used.
- Training should cover safe operating procedures, sling application, and troubleshooting.
- Regular competency assessments are essential to maintain safe practices.
- Selecting the Right Sling:
- Choose a sling that is appropriate for the patient’s size, weight, and condition.
- Ensure the sling is in good condition, free from tears or damage.
- Correct sling application is crucial for patient comfort and safety.
- Sling type is also important, different slings are made for different transfers, and patient needs.
- Conducting Pre-Transfer Checks:
- Inspect the hoist for any signs of damage or malfunction.
- Verify the battery charge (for electric hoists) or hydraulic fluid levels.
- Ensure the floor surface is clear and stable.
- Check the weight limit of the hoist and sling.
- Communicating with the Patient:
- Explain the transfer process to the patient in a clear and reassuring manner.
- Maintain eye contact and provide verbal cues throughout the transfer.
- Address any concerns or anxieties the patient may have.
- Performing the Transfer:
- Position the hoist and sling according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Lift the patient smoothly and slowly, avoiding sudden movements.
- Ensure the patient is securely positioned before moving them.
- Lower the patient gently onto the destination surface.
- Regular Maintenance and Servicing:
- Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for maintenance and servicing.
- Schedule regular inspections by qualified technicians.
- Replace worn or damaged parts promptly.
Investing in Safety and Dignity
Powered patient hoists are an invaluable tool for caregivers, providing a safe and dignified transfer experience for individuals with limited mobility. By adhering to best practices and prioritizing safety, we can ensure that these devices are used effectively to enhance the quality of care.
By implementing these guidelines, healthcare providers and home caregivers can significantly reduce the risks associated with patient transfers, promoting a safer and more comfortable environment for everyone involved.