As we age, maintaining good oral health becomes increasingly important. Not only does it contribute to a bright smile and fresh breath, but it also plays a crucial role in our overall well-being. Poor oral health can have significant implications for seniors, affecting not just their mouths but their entire bodies.
The Link Between Oral Health and Overall Health
Research has shown a clear connection between oral health and systemic health. Oral health issues, such as gum disease and tooth decay, can increase the risk of developing various systemic diseases, including heart disease, diabetes, and respiratory infections. This is because the mouth serves as a gateway to the rest of the body, and bacteria from oral infections can enter the bloodstream, causing inflammation and other health complications.
Common Oral Health Issues in Seniors
Gum Disease
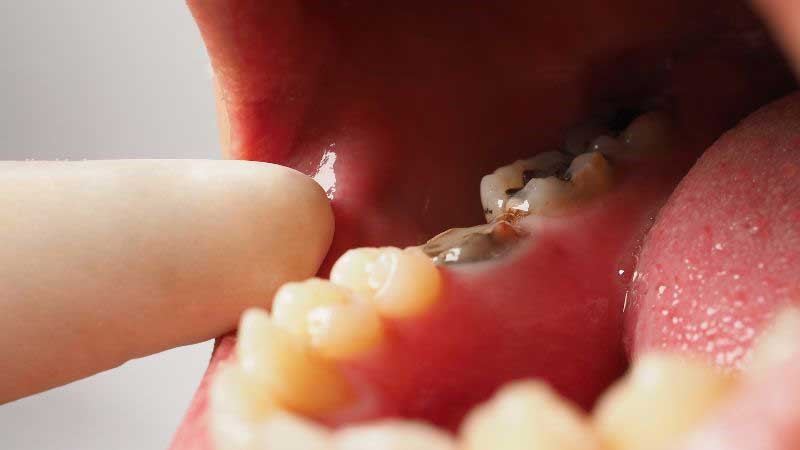
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a prevalent oral health problem among seniors. It occurs when plaque and tartar build-up along the gumline, leading to inflammation and infection of the gums. If left untreated, gum disease can progress to more severe stages, causing tooth loss and damage to the surrounding bone.
Tooth Decay
Tooth decay, or cavities, can affect individuals of all ages, but seniors may be particularly susceptible due to factors such as receding gums and dry mouth. Decay occurs when bacteria in the mouth produce acids that erode the enamel, leading to the formation of cavities. Without proper dental care, decay can progress and result in pain, infection, and tooth loss.
Dry Mouth
Dry mouth, or xerostomia, is a common issue among seniors, often caused by medications, medical conditions, or reduced saliva production with age. Saliva plays a crucial role in protecting the teeth and gums by washing away food particles and neutralizing acids. When saliva levels are low, seniors may experience discomfort, difficulty chewing and swallowing, and an increased risk of oral health problems.
Impact of Poor Oral Health on Seniors’ Overall Well-being
Nutrition and Diet
Poor oral health can impact seniors’ ability to eat a healthy and balanced diet. Painful gums, missing teeth, or ill-fitting dentures can make chewing difficult, leading to dietary restrictions and nutritional deficiencies. This can weaken the immune system, impair wound healing, and increase the risk of chronic diseases.
Quality of Life
Oral health problems can significantly affect seniors’ quality of life, causing pain, discomfort, and embarrassment. Difficulty speaking, smiling, or socializing due to dental issues can lead to feelings of isolation and depression, impacting mental and emotional well-being.
Mental Health
There is a growing body of evidence linking poor oral health to cognitive decline and dementia in seniors. Chronic inflammation and bacterial infections in the mouth may contribute to the development of neurodegenerative diseases, affecting memory, cognitive function, and overall brain health.
Strategies for Maintaining Good Oral Health in Seniors
Regular Dental Check-ups
Routine dental visits are essential for seniors to detect and address oral health issues early. Dentists can perform comprehensive exams, cleanings, and treatments to prevent or manage gum disease, decay, and other problems. Regular check-ups also provide an opportunity to discuss any concerns or changes in oral health.
Proper Oral Hygiene Routine
Seniors should follow a consistent oral hygiene routine to keep their mouths healthy. This includes brushing teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste, flossing daily to remove plaque and food particles between teeth, and using an antimicrobial mouthwash to reduce bacteria and freshen breath.
Healthy Lifestyle Habits
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can promote good oral health in seniors. Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins provides essential nutrients for healthy teeth and gums. Limiting sugary snacks and beverages helps prevent cavities, while staying hydrated encourages saliva production and reduces dry mouth symptoms.
Conclusion
In conclusion, poor oral health can have far-reaching effects on a senior’s overall health and well-being. By understanding the link between oral health and systemic health and taking proactive steps to maintain good oral hygiene, seniors can enjoy better oral health outcomes and a higher quality of life as they age.
FAQs
- Is it normal for seniors to experience dry mouth?
– Yes, dry mouth is common among seniors and can be caused by various factors such as medications, medical conditions, and reduced saliva production with age.
- How often should seniors visit the dentist?
– Seniors should visit the dentist at least twice a year for routine check-ups and cleanings, or more frequently if they have specific oral health concerns.
- Can poor oral health impact a senior’s ability to eat?
– Yes, oral health problems such as gum disease, tooth decay, and missing teeth can make chewing and swallowing difficult, affecting seniors’ ability to eat a healthy and balanced diet.
- What can seniors do to prevent gum disease?
– Seniors can prevent gum disease by practicing good oral hygiene, including brushing and flossing daily, visiting the dentist regularly, and avoiding tobacco use.
- How does poor oral health affect seniors’ mental health?
– Poor oral health can impact seniors’ mental health by causing pain, discomfort, and embarrassment, leading to feelings of isolation, depression, and anxiety.